![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Social Ecological Resilience](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jian_Hua3/publication/324682593/figure/fig1/AS:675114010038273@1537971131599/Social-Ecological-View-of-Psychological-Resilience.png)
Social Ecological Resilience Video
Understanding social-ecological systemsSocial Ecological Resilience - all
Recognition of the central role humans now occupy in the biosphere has led to calls for the definition of a new geologic epoch, the Anthropocene Crutzen In ecology, this has corresponded with interest in novel ecosystems e. Coupled human and natural systems are characterized by heterogeneity, cross-scale interactions, feedback loops, and dramatic shifts between multiple quasi-equilibrium states when certain thresholds are crossed, resulting in complex nonlinear dynamics that hamper predictions of system behavior Costanza et al. Resilience theory has come to dominate the CHANS literature as a way to promote sustainability by managing for resilience in the face of this uncertainty Brown , Folke et al. The interdisciplinary nature of resilience theory within CHANS has resulted in diverse theoretical contributions and frameworks reviewed in Folke and Folke et al. Resilience has been defined in multiple ways Quinlan et al. Hodgson et al. In the CHANS literature, resilience is generally equated with the concept of ecological resilience but can be expanded to include social adaptability e. Social Ecological Resilience.Introduction and Background: the Need for Resilient Decision-Making for Sustainable Circularity
The fashion and textiles industry, and policymakers at all levels, are showing an increased interest in the concept of circular economy as a way to decrease business risks and negative environmental impacts. The current material focus has several shortcomings, because fashion is a social-ecological system and cannot be understood merely by Social Ecological Resilience its environmental dimensions.
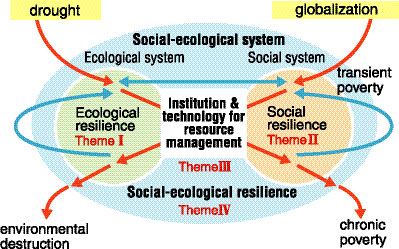
In this paper, we rethink the fashion system from a critical social-ecological perspective. The driver-state-response framework shows social drivers and ecological impacts as an adaptive social-ecological system, exposing how these interacting aspects need to be addressed for sustainable and resilient implementation of circular economy. We show how current responses to global sustainability challenges Social Ecological Resilience so far fallen short. Our overall aim is to expand possibilities for reframing responses that better reflect the complex links between the global fashion system, culture and creativity and the dynamics of the living planet. Resilient decisions aiming for sustainable circularity of the fashion industry must therefore pay attention to social activities beyond the industry value chain, not just material flows within it.
The sector has become a sizeable global industry, but increased production and consumption have accelerated material throughputs and increased disposal and waste, contributing to environmental changes at planetary scale. The industry is projected to recover from the pandemic and continue to grow Social Ecological Resilience 456 ]. Unless concerted efforts are made, its damaging environmental effects are expected to increase.

Figure 1 shows that since the production of polyester and cotton and the consumption of clothing have steadily increased, all in line with an increasing world GDP. Figure 1 also shows the rise in carbon emissions and the loss of biodiversity since to which the fashion industry has been a significant contributor.
Growth trends in production, consumption, environmental impacts and industry initiatives. Scales of the y -axis for each chart start at the value. Data sources: http://rmt.edu.pk/nv/custom/using-open-data-for-business-choices/selena-sardothiens-heir-of-fire.php production [ 7 ]; cotton production [ 8 ]; World GDP [ 9 ]; clothing consumption [ 10 ]; carbon dioxide emissions [ 11 ]; Red List species [ 12 ]; sustainable fashion initiatives [ 1314 ].
Along with engaging in initiatives for sustainable fashion, businesses are also increasingly referring Ecologiczl circular economy as the basis of their response. Principles of circular economy [ 1617 Theory Trauma emphasise closed-loop, regenerative material cycles, as a means to maintain access to resources and extend Resiliencw of goods. As such circular economy provides a way to reduce negative environmental impacts of the industry and by Ecologcal also decrease business risks. Businesses often describe their intention to move the industry Social Ecological Resilience a so-called take-make-waste business model — a shorthand for describing the linear value chain — towards a circular model to reduce negative social and environmental impacts from production and consumption.
Obviously the industry faces major technical challenges due to the global scale of the industry and its Social Ecological Resilience flows [ 1819 ] see also Fig. Studies on how and why fashion is used emphasise that non-material aspects of fashion, such as cultural values and social norms, are important determinants of fashion user decisions. A Swedish study found that clothes are disposed not because of their material condition but due to non-material aspects [ 24 ]. This relationship can Social Ecological Resilience conceptualised in terms of complex adaptive social-ecological systems [ 27 ].
Connect with Michelle
The nestedness of the system across scales means that all aspects of importance to human societies such as economy, justice and equality are shaped, Social Ecological Resilience dependent on and coevolve with the biosphere. In this paper, we take a social-ecological approach and focus on sustainability in its broad overarching sense as seeking harmony among human beings and between nature and humans [ 29 ].
We here bring together aspects of circularity, fashion and global sustainability, which is still a poorly charted terrain, and concentrate on the relationship between social and ecological issues in business responses to the unsustainability of the global Sodial industry. One important way link which businesses take action to decrease their negative impacts is by engaging Resiliehce various initiatives working for sustainability.
But, seen from a social-ecological systems perspective, most of the international initiatives for sustainable fashion which businesses engage Social Ecological Resilience focus on material ecological aspects.
INTRODUCTION
By doing so, they fail to recognise the intertwined nature of social-ecological systems. This failure has three shortcomings:. Different kinds of social actors have different capacities to change their own behaviour and that of the system as a whole. It contributes to a lack of recognition Social Ecological Resilience the social contexts of changes in Resillience conditions. Many decisions have different consequences depending on their specific place and context. In this paper, we first describe the key concepts and present the driver-state-response framework which structures our analysis and helps us to clarify the causal links between social drivers, environmental conditions and options for social actions.

We want to see if the objectives of these Social Ecological Resilience by the fashion industry to global sustainability challenges can show why the global fashion industry has so far fallen short of decreasing its overall negative impacts on people and the planet. In the third section, we apply the driver-state-response framework, coding the initiatives as responses that focus on social drivers click here environmental statesand in the final section, we outline Social Ecological Resilience insights for strategic decision-making for sustainability from a critical social-ecological perspective.
We argue that the biophysical and social dimensions of the fashion http://rmt.edu.pk/nv/custom/evaluating-the-limitations-of-market-research/the-worlds-of-human-geography-and-physical-geography.php should be brought into the same social-ecological system perspective because the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes increases when responses are based on an adaptive social-ecological system perspective. This paper thus seeks to contribute to both research understanding of how to think about fashion as a complex adaptive social-ecological system which is also useful for business decision on engaging in resilient responses which have to add up to a sustainable fashion system. Throughout the paper, we refer to sustainable circularity as a key concept.]
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured.
Why also is not present?